OnCore Nutrition - Two Peas in a Podcast
Episode 23: Antioxidants: keeping you feeling (and looking) young forever!
Episode Summary
Can you really keep eating red wine and eat dark choc guilt free?
Episode Notes
Disease prevention
Heart disease
- Vitamin E (almonds, peanuts, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds, avocado) and Beta Carotene (sweet potato, dark leafy greens, cantelope, capsicum) are often studied as it is hypothesized that these antioxidants can prevent the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques.
- Results of larger trials haven’t shown as profound as we had hoped for, however we have rational for this!
- Women’s Health Study - 39,876 healthy women took 600 IU of natural source vitamin E or a placebo every other day for 10 years.
- The study did not see a reduction in CVD events, however it did find a 24% reduction in total cardiovascular mortality.
- Women’s Antioxidant Cardiovascular Study - 8,171 women randomised.
- looked at beta-carotene, vitamin E, vitamin C.
- Modest benefit for vitamin E among women with existing cardiovascular disease.
- Women in the active vitamin C and E experienced fewer strokes
- Patients taking vitamin E had significantly more heart failure. Vitamin E was linked to a 13% higher risk of heart failure and a 21% increased risk of hospitalization for heart failure
- Lott, E. The Journal of the American Medical Association, March 16, 2005; vol 293: pp 1338-1347. Brown, B.G. The Journal of the American Medical Association, March 16, 2005; vol 293: pp 1387-1390.
- .https://academic.oup.com/ajcn/article/69/6/1322S/4715025
- a recently published analysis of clinical trials involving nearly 136,000 people who took vitamin E for one reason or another found that the overall risk of dying was greater in those who took higher doses, compared to those who took lower doses.
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/press_releases/facts_about_vitamine
- Not a huge benefit when it comes to supplementation - this was also supported in a very highly regarded medical journal called The Lancet. We know that antioxidants in fruits and vegetables, which also contain valuable fibre can have a profound impact on heart health and prevention of heart disease.
Cognitive conditions (dementia, alzheimers)
- Oxidative stress caused by free radical damage can contribute to brain aging, cognitive deterioration and conditions such as alzheimers or dementia. .
- The literature has some mixed results, however again we know there is more to this complex puzzle.
- Prevention of Alzheimer's Disease by Vitamin E and Selenium Trial (PREADViSE).
- This study aimed to determine if vitamin E or selenium supplements used alone or in combination can prevent dementia older men.
- 3,700 men aged 60 or older for 6 years
- Unfortunately the antioxidant supplements did not prevent the onset of Alzehimers disease.
- Physicians' Health Study II (PHSII), - 5,956 men age greater than 65 years.
- The average treatment duration was 18 years - very long!
- Subjects were given 50 mg beta-carotene supplements or a placebo.
- Long term supplementation showed positive cognitive outcomes.
Statement by the Alzheimers Society regarding use of antioxidants:
“Though lab-based experiments on different types of antioxidants seem promising, there is only limited support for the claims that antioxidants may protect against Alzheimer's disease from studies involving people.
However, increasing fresh fruit and vegetables in the diet has numerous benefits aside from increasing antioxidant intake and is highly recommended, especially as part of a Mediterranean diet”
We know there is data to suggest that eating a Med type diet (which is rich in antioxidants) is beneficial in reducing the risk of dementia.
Cancer
We know that eating a diet rich in antioxidant rich fruit and vegetables and protective against a range of different cancers. Whilst there are some gaps in the literature there are some really exciting trials currently underway.
Longevity & anti-aging
If we can prevent the onset of chronic diseases through increasing our intake of antioxidants, we can lead a healthier life for longer!
“Free Radical Theory of Aging” (FRTA), also known as “oxidative damage theory of ageing” is a concept that free radicals and other reactive oxygen species are a byproduct of metabolism and occurs as a result of a number of exogenous factors; and it is the accumulation of damaged cells are the reason we experience age-related diseases and aging. Why antioxidants are of interest in terms of aging and longevity, is because they can block or downregulate these damaging pathways.
http://www.actabp.pl/pdf/2_2000/281.pdf
There are a number of different antioxidants that are of interest when we focus on anti-aging. These include - Ascorbic acid (Vit C), alpha-tocopherol (Vit E), Ubiquinol (Coenzyme Q10), Melatonin, Curcumin, resveratrol, etc..

Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3982418/
Ubiquinol (Coenzyme Q10)
- It is a unique lipid-soluble antioxidant and is essential for mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC), which is a fancy way of referring to energy production within our cells.
- Benefits from heart disease risk, kidney disease, inflammation, fertility, aging, metabolic syndrome.
- In regard to CVD a cochrane review in 2014 found that supplementing with Co-Q10 showed a significant reduction in systolic blood pressure without improvements in other CVD risk factors, such as diastolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, LDL- and high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol, and triglycerides.
- Endothelial function
- Inflammation - Meta-analysis explored the effect of CoQ10 on C-reactive protein (inflammatory measure), interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) in patients with inflammatory conditions such as multiple sclerosis, obesity, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, etc... It found that Co-Q10 doses between 60 to 500 mg/day for a 1-week -4-months significantly reduced production of inflammatory cytokines.
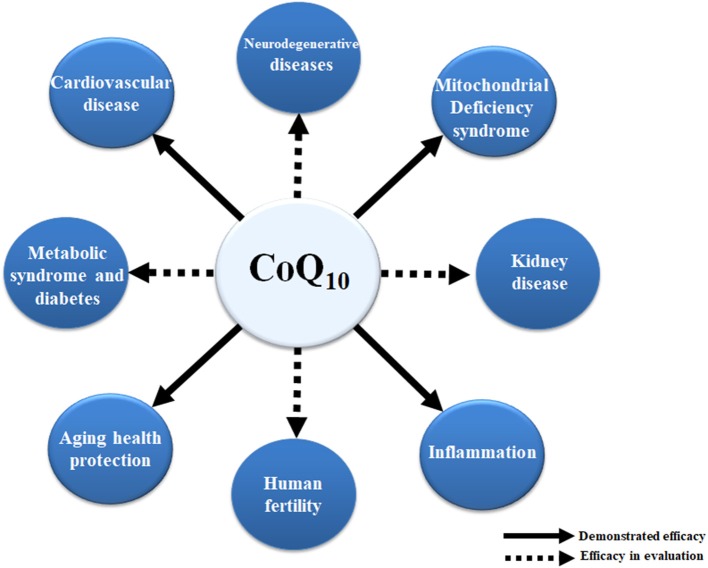
Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5807419/#B39
Food sources:
- Organ meats: Heart, liver and kidney
- Some muscle meats: Pork, beef and chicken
- Fatty fish: Trout, herring, mackerel and sardine
- Vegetables: Spinach, cauliflower and broccoli
- Fruit: Oranges and strawberries
- Legumes: Soybeans, lentils and peanuts
- Nuts and seeds: Sesame seeds and pistachios
- Oils: Soybean and canola oil
Resveratrol (RSV) - A polyphenolic compound that stimulates cell defense pathways.
- Protects these plants against UV rays and some fungal infections.
- It has been hypothesised that it is RSV that is responsible for the ‘French paradox’ - low rates of heart disease in France, despite a diet rich in cheese and red wine.
- There is evidence that resveratrol may be beneficial in the context of diabetes, CVD and cancer.
- Meta Analysis which looked at the evidence regarding RSV across a number of different species. It found that there are a few species that found life extension in response to RSV.
- Metabolic function
- Be careful of high doses of resveratrol if history of breast cancer
- Food sources: Red wine, grapes, peanuts, pistachios, dark choc, cacao, strawberries